basal tear secretion test|The Tearing Patient: Diagnosis and Management : services The Schirmer test is objectively used to measure tear secretion. The test is performed by placing a porous filter strip in the inferior fornix of each unanesthetized eye for 10 minutes. A healthy . An autoclave is the most common method of sterilization in the laboratory working on moist heat. Sterilization is the process of removing or destroying all microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, and their spores .Copyright Disclaimer Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for "fair use" for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research. Fair use .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Sterilization autoclaves are widely used in microbiology and mycology, medicine and prosthetics fabrication, tattooing and body piercing, and funerary practice. They vary in size and function depending on the media to be sterilized and are sometimes called retort in the chemical and food industries. Typical loads include laboratory glassware, other equipment and waste, surgical instruments, and
The Schirmer tear test assesses the amount of tears in the eyes and is frequently used to diagnose dry eye syndrome. Basal and reflex tear . There are two variations of the Schirmer test: Schirmer I measures total tear secretion (basal and reflex). Schirmer II is a measure of reflex secretion only and involves .
There is some debate about the reliability of testing to evaluate tear production, but we find it useful to assess the basal tear secretion. This is done by placing a strip of filter paper .The test works by the principle of capillary action, which allows the water in tears to travel along the length of a paper test strip in an identical fashion as a horizontal capillary tube. The rate of travel along the test strip is proportional to the rate of tear production. The patient is instructed to look upward, and the patient’s eyelid is pulled down. The bent end of the test strip is placed in the e.The Schirmer test is objectively used to measure tear secretion. The test is performed by placing a porous filter strip in the inferior fornix of each unanesthetized eye for 10 minutes. A healthy .Schirmer's test measures total tear secretion, including reflex, and basal tears. The test is known to measure reflex tears without anesthesia and basal tears with anesthesia ( 23 – 25 ). .
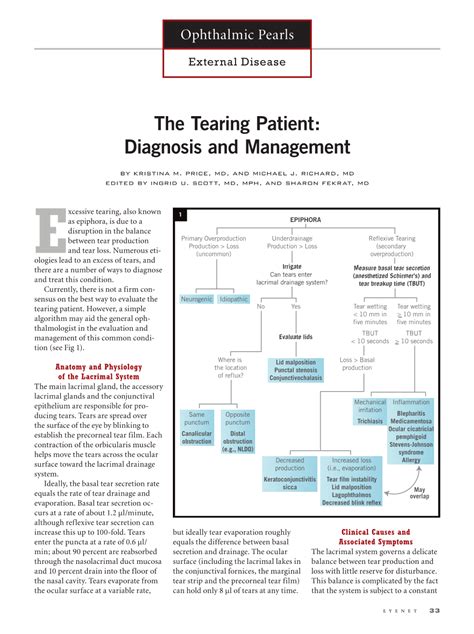
The Tearing Patient: Diagnosis and Management
The Schirmer tear test performed with and without anesthesia evaluates tear adequacy and often aids in the diagnosis of dry eye syndrome. The Schirmer test performed without anesthesia .
7180 chemistry analyzer
Schirmer's test is used to determine whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist. The test is performed by placing filter paper inside the lower lid of the eye. After 5 minutes, the .The Basic Tear Secretion Test is used to measure basal tear volume (without reflex component). They are tools that can be used as part of a dry eye workup. Indications. Patient complaint of .
(Schirmer’s test is also known as the dry eye test, the tear — or tearing — test and the basal secretion test.) The eyes’ natural tears are produced by special cells in the conjunctiva and by the lacrimal and meibomian glands. The Schirmer tear test assesses the amount of tears in the eyes and is frequently used to diagnose dry eye syndrome. Basal and reflex tear secretion are measured together using the non-anesthetized Schirmer test or when the test is carried out without anesthesia. There are two variations of the Schirmer test: Schirmer I measures total tear secretion (basal and reflex). Schirmer II is a measure of reflex secretion only and involves nasal stimulation following insertion of the strip.
There is some debate about the reliability of testing to evaluate tear production, but we find it useful to assess the basal tear secretion. This is done by placing a strip of filter paper in the conjunctival fornix after administering topical anesthetic drops.Schirmer's test uses paper strips inserted into the eye for several minutes to measure the production of tears. Both eyes are tested at the same time. Most often, this test consists of placing a small strip of filter paper inside the lower eyelid (inferior fornix).The Schirmer test is objectively used to measure tear secretion. The test is performed by placing a porous filter strip in the inferior fornix of each unanesthetized eye for 10 minutes. A healthy eye should wet more than 15 mm of the standard filter strip in 5 minutes.Schirmer's test measures total tear secretion, including reflex, and basal tears. The test is known to measure reflex tears without anesthesia and basal tears with anesthesia ( 23 – 25 ). However, the concept of basal tears is uncertain.
Schirmer's test is used to determine whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist. The test is performed by placing filter paper inside the lower lid of the eye. After 5 minutes, the paper is removed and tested for its moisture content.The Basic Tear Secretion Test is used to measure basal tear volume (without reflex component). They are tools that can be used as part of a dry eye workup. Indications. Patient complaint of dry eyes or suspected dry eyes. Contra-Indications. Allergy to topical ocular anesthetic, if used. Materials. Schirmer Tear Test strips.The Schirmer tear test performed with and without anesthesia evaluates tear adequacy and often aids in the diagnosis of dry eye syndrome. The Schirmer test performed without anesthesia measures basal tear secretion and reflex tear secretion.
(Schirmer’s test is also known as the dry eye test, the tear — or tearing — test and the basal secretion test.) The eyes’ natural tears are produced by special cells in the conjunctiva and by the lacrimal and meibomian glands. The Schirmer tear test assesses the amount of tears in the eyes and is frequently used to diagnose dry eye syndrome. Basal and reflex tear secretion are measured together using the non-anesthetized Schirmer test or when the test is carried out without anesthesia.
There are two variations of the Schirmer test: Schirmer I measures total tear secretion (basal and reflex). Schirmer II is a measure of reflex secretion only and involves nasal stimulation following insertion of the strip. There is some debate about the reliability of testing to evaluate tear production, but we find it useful to assess the basal tear secretion. This is done by placing a strip of filter paper in the conjunctival fornix after administering topical anesthetic drops.Schirmer's test uses paper strips inserted into the eye for several minutes to measure the production of tears. Both eyes are tested at the same time. Most often, this test consists of placing a small strip of filter paper inside the lower eyelid (inferior fornix).The Schirmer test is objectively used to measure tear secretion. The test is performed by placing a porous filter strip in the inferior fornix of each unanesthetized eye for 10 minutes. A healthy eye should wet more than 15 mm of the standard filter strip in 5 minutes.
Schirmer's test measures total tear secretion, including reflex, and basal tears. The test is known to measure reflex tears without anesthesia and basal tears with anesthesia ( 23 – 25 ). However, the concept of basal tears is uncertain.Schirmer's test is used to determine whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist. The test is performed by placing filter paper inside the lower lid of the eye. After 5 minutes, the paper is removed and tested for its moisture content.
The Basic Tear Secretion Test is used to measure basal tear volume (without reflex component). They are tools that can be used as part of a dry eye workup. Indications. Patient complaint of dry eyes or suspected dry eyes. Contra-Indications. Allergy to topical ocular anesthetic, if used. Materials. Schirmer Tear Test strips.
Les poteaux bois carrés ont une longueur de 2,00 mètres et sont faits de bois de pin imprégné classe 4 vert, ce qui les rend résistants intempéries, aux insectes xylophages et aux champignons. Les poteaux carrés lisses peuvent être .
basal tear secretion test|The Tearing Patient: Diagnosis and Management